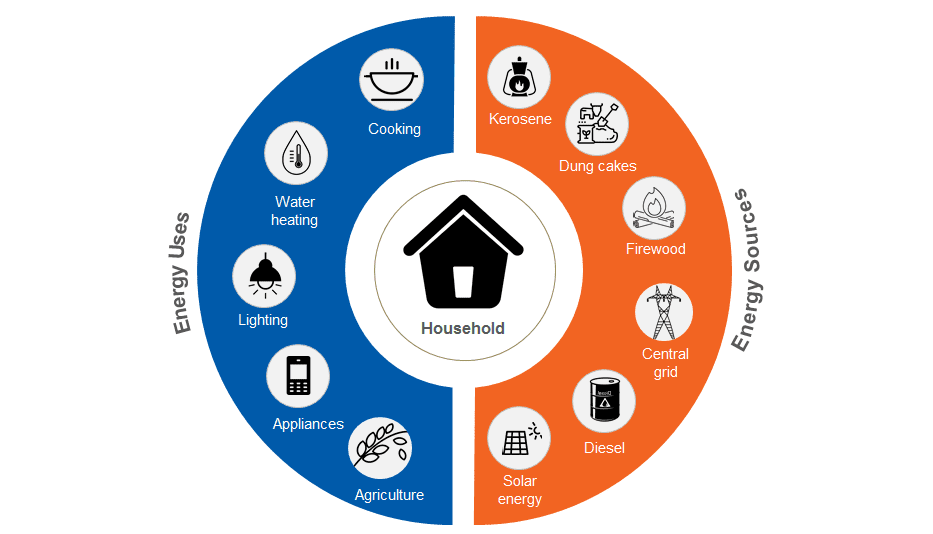
Limited access to clean and safe energy sources such as solar or grid electricity remains a critical problem for millions of rural Indian households. More than 240 million people depend on traditional, inefficient biomass fuels for lighting, running appliances, cooking, and economic uses.
In recent years, the advent of cleaner and safer energy solutions, coupled with appropriate financing supports in certain areas, has increased access for many. Even so, our research suggests that many households have not transitioned entirely to these cleaner and safer options, but rather continue to use a diverse range of sources.
There is currently limited understanding of this complex reality for rural energy customers. As a starting point to build a consumer-centric view of the gap that exists between energy needs and the use of modern sources, we synthesized data from 500 energy-poor households and interviewed more than 120 families to understand how they service their multiple energy needs.
Top Takeaways
- Customer preferences in their energy source choices tend to be overlooked. Previous research has not taken a consumer-centric view, making it difficult to change customer behavior.
- Our focus must shift from introducing new sources into households to increasing customer preference and usage.
- Improving demand for clean energy sources could have enormous positive results—for example, by shifting the method of cooking from biomass to induction.