Inadequate access to sanitation and the resultant transmission of communicable diseases remains a significant problem globally. Public finance alone cannot meet the scale of investment required and market-based sanitation (MBS) is increasingly viewed as a promising approach for scaling the delivery of onsite sanitation through the private sector.
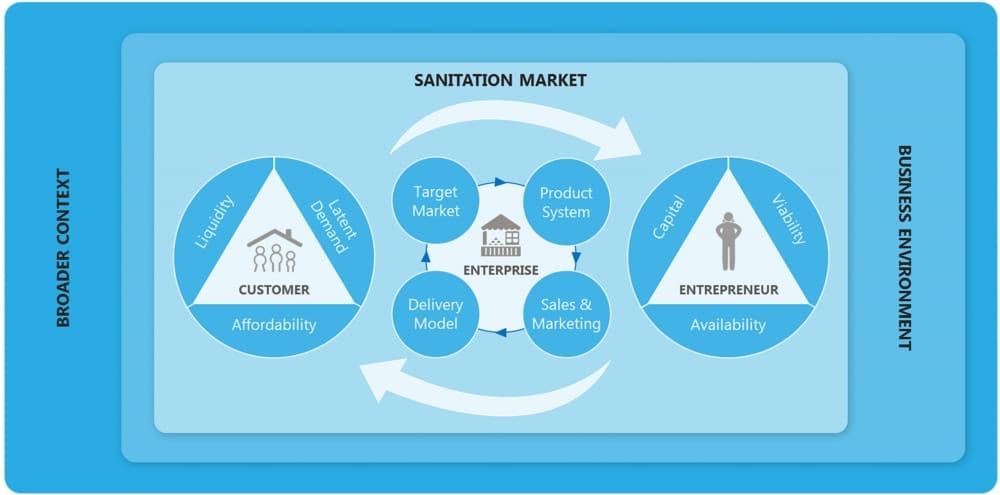
This desk review establishes a framework to analyze, design, and improve MBS interventions and offers guidance to stakeholders interested in using markets to increase sanitation coverage and end open defecation. The review also highlights the broader contextual parameters that determine the applicability of MBS as an approach within a given market.
Top Takeaways
- MBS interventions can scale up if funders remain invested beyond the typical 3-to-5 year funding cycles. At-scale MBS Interventions find toilet sales begin to rise 4 to 5 years after initiation of the interventions during which locally appropriate enterprise and intervention models have been developed and refined.
- To ensure sustainability of the market, implementers should actively build in self-redundancy in intervention design to maximize the likelihood that the market continues to function even as donors and funders exit the market.
- Implementers should consider and account for scaling barriers in the business environment when designing MBS interventions. Funders should address these barriers to create an enabling business environment for entrepreneurs by investing in public goods and advocating for changes in formal market rules.
- Funders should recognize that MBS may be a necessary but not sufficient intervention to spur the delivery of toilets in some contexts meaning that it represents one among a suite of preferred approaches. Broader contextual factors such as social norms, geographic conditions, and transport infrastructure determine the effectiveness of MBS in a given market.